
Height maps can make for incredible surface detail and noise, without actually affecting or adding more geometry. Height maps are incredibly valuable for realism in your images and this can not be overstated enough! Furthermore, the brightness of Displacement maps cannot be further adjusted or inverted when editing the texture inside the Enscape Material Editor itself. It’s worth noting that Displacement maps are incompatible with transparent materials so the entire “Transparency” section becomes unavailable where a displacement map has been applied (including mask textures). The actual technique employed in Enscape is called quadtree parallax displacement mapping for optimum performance. Normally an Occlusion Map is the type of image you will use for Displacement maps. These RGB components correspond to the X, Y, and Z coordinates, respectively.ĭisplacement maps are an enhancement of the bump mapping or normal mapping techniques applied to textures. Normal map are a type of Bump map that require an image with RGB values. They tell Enscape to interpret a surface as protruding (bright parts of the texture) or recessed (dark parts of the texture). The Height option in the Enscape Material Editor allows you to utilize so called Bump, Normal, or Displacement maps in order to simulate bumps, wrinkles and dents and the lighting of these.īump maps can be any black and white 2D images. The amount by which it’s blurred is being determined by the Roughness value in the Reflections area. If the Frosted Glass checkbox is enabled, Enscape will blur what’s visible through the transparent surface.
#Cara memasukan file ke cd free
You know this effect from looking at a glass of water, or very thick glass.Īir has a refractive index of 1.0 – so light rays travel through it in a straight line -, water has an index of 1.33, window glass 1.52, and, for example diamonds have an index of 2.42 – they bend light quite heavily.įor further information on this topic, feel free to have a look at the Wikipedia article.

The Refractive Index slider determines by which factor light is being bent when traveling through a transparent surface. This menu allows you to choose a color that should be added to any semi-transparent areas of your material.

If you’re using it combined with a transparency map, it will define the maximum opacity, so white areas on said map will appear as opaque as you’ve set using this slider. The Opacity slider controls the overall transparency of the surface. If you load a colored image, Enscape will automatically convert it to black and white, so you don’t have to worry about that. Grey areas will appear partially transparent, such as glass. It refers to the Opacity value, so a black area (which equals zero) on the image used will result in a perfectly transparent portion of the surface, while a white area will appear perfectly opaque. Your membership fee will directly support and inspire Mohammad Masumand and thousands of other writers you read.The Texture parameter allows you to control the transparency using a 2D image, a map. (and thousands of other writers on Medium). Read every story from Mohammad Masum, Ph.D.
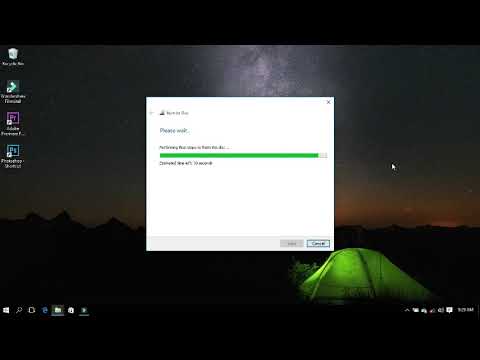
#Cara memasukan file ke cd how to
Given that the name of the dataframe is “sample”, then save the file in Google Drive using one line code: sample.to_csv('sample.csv')įinally, to download in the local drive execute the following single line code: files.download('sample.csv')Īs an additional source, you can also read this blog to understand more about how to deal with files in Colab.
We can easily download data into local directories by executing the following two lines of codes given the dataset is already in CSV format: from lab import files files.download('sample.csv')Ī pandas dataframe can be downloaded by executing the following code. Running the shell will return a URL link and ask for an authorization code:įinally, we can read the data using a library like Pandas: pd.read_csv("sample.csv")ĭownloading Data into Google Drive and Local System
#Cara memasukan file ke cd code
Step 1 To connect Google Drive (GDrive) with Colab, execute the following two lines of code in Colab: from lab import drive drive.mount("/content/gdrive") Mounting Drive into the Colab meaning that setting up the google drive account as a virtual drive so that we can access the resources of the drive just like a local hard drive. We can access files in the drive using mounting Google Drive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
